- A natural satellite
- Receives its light from the sun and reflects it onto the earth.
- It revolves around the earth
- Takes 29.5 days to complete one revolution around the earth
- Its orbit is almost circular
- As it revolves around the sun it appears in various shapes ranging from
crescent/new moon,
half moon,
gibbons moon and
full moon.
- Has gravitational pull which causes the rising and falling of the ocean level
- As the moon orbits around the earth it creates an event called eclipse.

Eclipse
- Phenomenon occurring when the rays of the sun are blocked from reaching the earth or the moon.
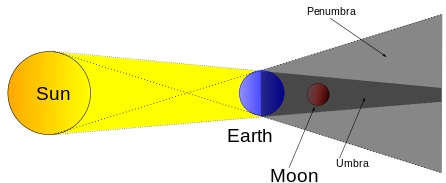
Solar/Sun Eclipse
- The moon comes between the earth and the sun
- The moon's shadow is cast on the earth
- The sun appears to be covered by darkness
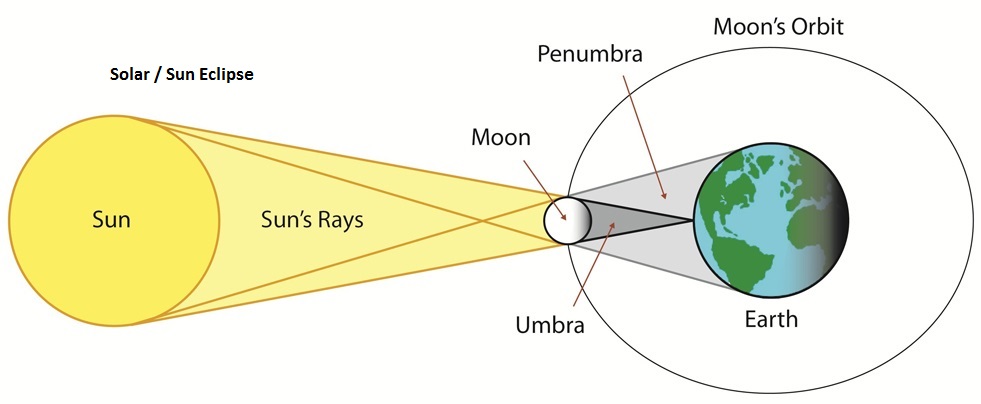
Lunar/moon Eclipse
- The earth comes between the moon and the sun
- The earth's shadow is cast on the moon
- The moon appears to be covered by darkness