a. Contraction Theory
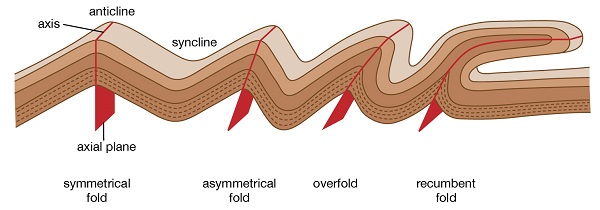
- During the earth’s formation surface rocks cooled faster and wrinkled to form Fold Mountains.
b. Convectional Currents Theory
- Horizontal convectional currents in the mantle exerted frictional pull on crustal rocks.
- Continental crusts were pulled towards each other.
- Sediments between them were squeezed into folds.
c. Continental Drift Theory
- During break of Gondwanaland India drifted northwards and collided with Eurasia.
- Sediments between were squeezed to form fold mountains e.g. Himalayas and Everest.
d. Plate Tectonics Theory
- When an oceanic plate meets another or it meets a continental plate, the sediments under the sea are compressed to form Fold Mountains.
- When two continental plates meet the sial layer is compressed to form fold mountains
- E.g. Alps was formed when Africa plate pushed against the rigid European plate
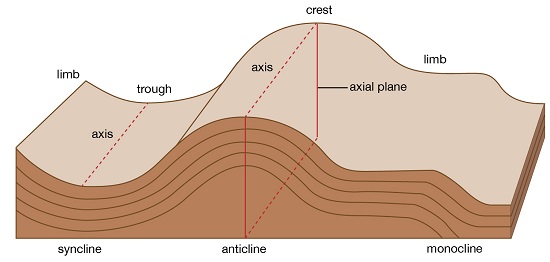
2. Escarpments

The Niagara Escarpment
- A relatively continuous line of steep slopes facing the same direction.
- Formed one compressional force causes folding resulting in one steep limp of
the anticline which forms the escarpment.
3. Depressions
Formed when not very strong forces cause folding causing some parts of the
earths surface to form synclines forming basins.
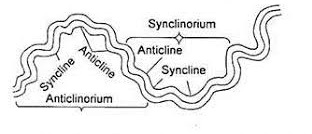
4. Ridges and Valleys
- When folding occurs anticlines form uplands/ridges/hills while synclines form
valleys.
5. Rolling Plains
- A high fairly level land between mountains.
- Formed when rocks at the edges of a region become intensely folded and the middle parts resist folding resulting into mountains which enclose a high fairly level land.
7.Inter-montane basins
-Formed when some parts of inter-montane plateau sink more to form basins.