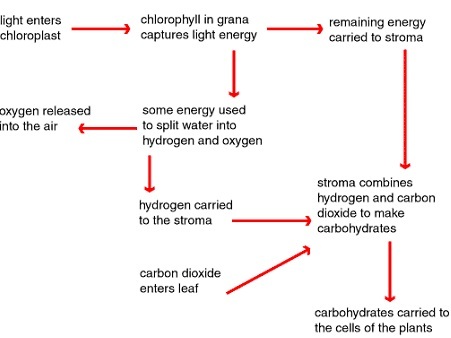
- These reactions are light independent. The energy that propels these reactions are derived from the ATP formed during light stage.
- Also known as carbon (IV) oxide fixation, dark stage involves combination of carbon (IV) oxide molecule with hydrogen ions to form a simple carbohydrate and a water molecule.
- Dark reactions take place in the stroma.
CO2 + 4H+ ----->(CH2O)n + H2O
- Other food materials are then synthesized from the simple sugars through complex synthesis reactions.
- The simple sugar formed in dark stage is quickly converted to starch which is osmotically inactive.
- When a lot of simple sugars accumulate in the chloroplasts, osmotic pressure of the guard cells would increase causing the guard cells to draw a lot of water through osmosis.
- This makes the guard cells to bulge and open the stomata.
- This can result into excessive water loss.
- To prevent, this, the simple sugars are quickly converted to starch.
- To test whether photosynthesis has taken place in a leaf, therefore, a test for presence of starch and not simple sugars is carried out.