Question 1
The diagram below shows a life cycle of a cockroach
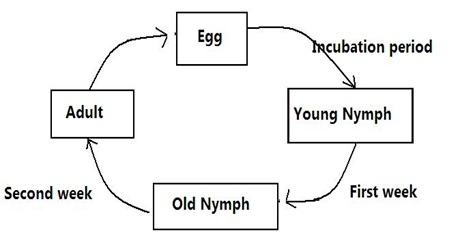
- Name the hormone that would be at high concentration during the first and second week and their functions.
- First week
Hormone
Function - Second week
Hormone
Function
- First week
- Name the structure that produces hormone named in a (ii) above
- Name the process represented by the life cycle above
- State two importance for the process named in (c) above
Answer
- Juvenile hormone
Function - forms larval cuticle/ inhibits moulting metamorphic effects of hormone in the larval stage. - Ecdysone / moulting hormone
Function - moulting to allow growth and metamorphosis
- Juvenile hormone
- Prothoracic gland
- Metamorphosis/ incomplete metamorphosis
- 1. It reduces competition for food since they feed on different food substances
2. Adapts the organism to escape adverse environmental conditions
Question 2.
The diagram below represents part of a gaseous system in a grasshopper.
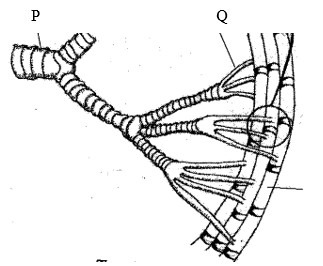
- Name the structures labeled P and Q
- P
- Q
- State the function of the structure labeled P
- Describe the path taken by carbon (IV) oxide from the tissues of the insect the atmosphere. \
- How is the structure labeled Q adapted to its functions.
Answer
-
- P - rings of chitin/ spiral bands
- Q - tracheoles
- Circular rings keep the trachea open when pressure is exerted inside the lumen is low.
- Carbon (IV) oxide is of high concentration in the muscle tissue therefore it diffuses from the tissues into the tracheoles and moves to the trachea and out through the spiracles into the atmosphere. \
- 1. The walls are thin and lack chitin for rapid diffusion of gases.
2. Walls are moist to dissolve gases.
3. They are highly branched to increase the surface area for gaseous exchange.
Question 3
The set up below illustrates an experiment to demonstrate a certain biological process, before the addition of the yeast suspension the glucose solution was first boiled and then cooled at 40oC.

- What was the aim of the experiment?
- What observations would you make in the tubes a few minutes after the experiment begun.
- Explain the observations made in (b) above
- Why was glucose solution boiled before cooling at 40oC
- How can you set up a control experiment for the above
Answer
- To show that coarbon (IV) oxide is produced during anaerobic respiration.
- There is production of bubbles in the boiling tube of carbon (IV) oxide leading to the formation of a white precipitate in the test tube containing calcium hydroxide solution.
- Yeast cells undergo anaerobic respiration prodicing carbon (IV) oxide gas which dissolves in calcium hydroxide solution forming a white precipitate; production of the gas results in bubbles.
- To kill other micro-organisms present in glucose solution thus eliminating microbial respiration.
- Through the use of glucose solution without yeast cells
Question 4
The following are short messages (sms) on cell phone communication between Mrs. Mkenzie and her husband. They can be used as analogies of gene mutation

- For each of these messages identify the type of gene mutation illustrated
- State one example of chromosomal mutation that lead to
- Change in chromosome structure
- Change in chromosomal number
- Explain why genetic counseling is termed as one practical application of genetics.
Answer
-
- Insertion
- Deletion
- Substitution
- Invertion
-
- Deletion, Duplication
- Non-disjuction
- It involves provision of information and advice on genetically inherited disorders, their risks and outcomes.
Question 5
The following is a photograph of s dissected mammal. Study the photograph and answer the questions that follows.

- Name the structures labeled R,S and T
- R
- S
- T
- On the photograph, label and name the site of production of vitamin K
- State one function of the following parts
- S
- T
-
- State the sex of the dissected mammal
- Give a reason for your answer in d (i) above
Answer
- Name the structures labeled R,S and T
- R - Liver
- S - Stomach
- T - Ileum
-

-
- S - Site of initial protein digestion/ site for temporary storage of food.
- T - Site of completion of digestion and absorption.
-
- Female
- Presence of uterus
