Question 1
A student set up an experiment using a visking bag as shown
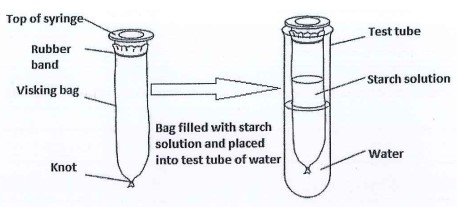
The student added some iodine solution to the water in the test-tube. After 30 minutes at room temperature, the contents of the visking bag were stained blue-black, but the water outside remained a yellow colour.
- Explain these results
- State factors that influence the movement of molecules through visking bag.
Answer
- Iodine solution / molecules diffused into the visking bag, iodine molecules are small enough to pass through the membrane; iodine solution react with starch; No starch diffused out of the bag through visking tubing; starch molecules are to large to pass through membrane.
- - Temperature
- Surface area
- Concentration gradient
Question 2
Use the diagram below to answer the questions that follow

- Name the parts labelled A, B and C
A
B
C - State the function of the part labelled C.
- What is the difference between pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation.
Answer
-
A - Sinoatrial (SA) node
B - Atrio-ventricular (AV) node
C - Vagus nerve (Parasympathetic nerve) - The vagus nerve (parasympathetic nerve) helps regulate the heart rate by decreasing the heart rate when activated. It works to counteract the effects of the sympathetic nervous system, which typically increases heart rate.
-
Circulation Type Pulmonary Circulation Systemic Circulation Pathway Heart → Lungs → Heart Heart → Body → Heart Blood Movement Deoxygenated blood from right ventricle to lungs; returns oxygenated to left atrium Oxygenated blood from left ventricle to body; returns deoxygenated to right atrium Purpose Oxygenate blood and remove carbon dioxide in the lungs Deliver oxygen and nutrients to tissues; remove waste and carbon dioxide
Question 3
What is the advantage of having a double circulatory system over a single circulatory system?
Answer
1. Oxygenation: Blood is pumped twice, ensuring strong delivery of oxygen.
2. Separation of Blood: Keeps oxygenated and deoxygenated blood apart for better oxygen transport.
3. Supports High Metabolism: Meets the energy needs of active, larger organisms.
4. Controlled Blood Pressure: Allows separate pressure regulation in lungs and body.
2. Separation of Blood: Keeps oxygenated and deoxygenated blood apart for better oxygen transport.
3. Supports High Metabolism: Meets the energy needs of active, larger organisms.
4. Controlled Blood Pressure: Allows separate pressure regulation in lungs and body.
Question 4
Study the sickle cell pedigree below and answer the questions that follow
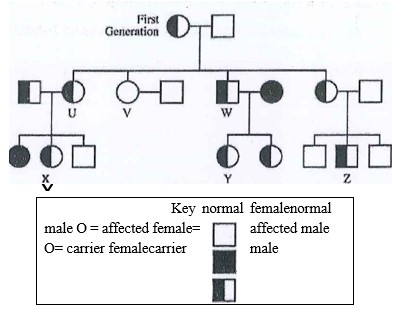
Given that the allele for normal haemoglobin is expressed as HbA while the allele for abnormal haemoglobin is HbS
a) Complete the genetic diagram of marriage of two X and Z
b) What is the probability of having a sickle cell child
c) Describe the effects of sickle cell anemia on the body
Answer
a) Punnett square
Possible offspring Genotypes:
b) The probability of having a child with sickle cell anemia (genotype HbSS) is 25%.
c)
| HbA(X) | HbS(X) | |
|---|---|---|
| HbA(Z) | HbAA | HbAS |
| HbS(Z) | HbAS | HbSS |
Possible offspring Genotypes:
- HbAA (Normal): 25% chance
- HbAS (Carrier): 50% chance
- HbSS (Sickle cell anemia): 25% chance
b) The probability of having a child with sickle cell anemia (genotype HbSS) is 25%.
c)
- Red blood cells become sickle-shaped, making them less flexible and more prone to getting stuck in blood vessels.
- The sickle cells carry less oxygen, leading to chronic fatigue and anemia.
- The misshapen cells can block blood flow, causing pain crises, organ damage, and increased risk of stroke.
Question 5
The figure below shows the human gas exchange system.

- Name structures K and L.
K
L - Explain how structure L is adapted to its function
- Tobacco smoke affects the gas exchange system. Name one components of tobacco smoke and describe their effect on the gas exchange system.
Component
Effect - Name the part of the blood in which most carbon (IV)oxide is transported.
Answer
- K- Bronchiole
L - Trachea - Their extensive branching increases the total surface area available for gas diffusion.
The walls of bronchioles are very thin, allowing gases to diffuse rapidly across them.
Bronchioles lead directly to alveoli, where the actual gas exchange takes place. - Component - Tar / Nicotine / Carbon (IV) Oxide
Effect - Causes lung cancer/ mutation. - Plasma
