There are natural and artificial sources of light
| Natural Sources |
Artificial Sources |
| Stars |
Lamps |
| Sun |
Torch |
| Fireflies |
Candles |
| Glowworms |
Bulbs |

A Glowworm - Natural Source of Light
The process of glowing is known as
bioluminescence
Basic uses of Light
- Photosynthesis in plants
- Sight
- Used in photography
- On roads, it is used for safety (traffic lights)
Properties of Light
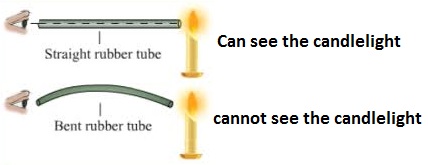
i) Light travels in a straight line from the source
The experiment below shows how light travels in a straight line:

The diagram (a) above, the observer can see the candlelight through the holes made on the cardboards A, B and C.
When cardboard B is moved, the observer can no longer see the candlelight as before. Examine the figure below.

Also, looking through a rubber tube as shown below follows the same principle.
ii) Light travels in all directions
- For an experiment, consider a bulb or a candle.
- A lit candle in a room shows light in all sides.
Reflection of Light
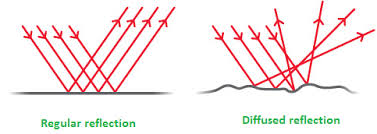
- Reflection is the bouncing back of light on the surfaces of objects.
- There are two types of refection:
Regular and
Irregular (Diffused) reflection of light.
Characteristics of Images on a Plane Mirror
- the image is virtual (not real)
- the distance between the object and the mirror is the same as the distance between the mirror and the image.
- the image is upright
- the image is laterally inverted

A periscope uses the principle of refection to observe things around corners. The mirrors are placed at 45°. Observer the image below

Refraction of Light
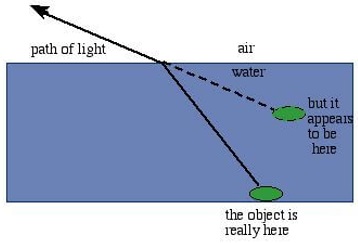
Refraction is the bending of light waves as it moves from one medium to another e.g from air to water.
Apparent bending refers to the bending of light at the surface of water as it moves from air to water.

From the image above, the pencil appears broken. From the image below, the coin appears raised.
 Attempt the experiments above to fully understand the effects of refraction of light.
Attempt the experiments above to fully understand the effects of refraction of light.
Effects of Refraction of Light
- A pool of water appears shallower
- A ruler appears broken when placed in water
- A coin in water appears raised
- Formation of a mirage (as seen on a road during shinny days)
The image below shows a road mirage. In a road mirage, there appears to be water on the road.

Dispersion of Light
Dispersion of light refers to the splitting of
white light into 7 different colours
The 7 colours form the spectrum. Can you name the 7 colours?
 Try to remember the colours in order
Try to remember the colours in order
Opaque, transparent and Translucent materials
-
Transparent materials allow light to pass through and you can see through them (e.g Air, Clear Glass, Clear water)
-
Translucent materials allow light to pass through but you cannot see through them clearly (e.g dirty water, oiled paper, plastics, frosted glass)
-
Opaque materials do not allow light to pass through them (e.g metal, stone, wood, iron sheet).













