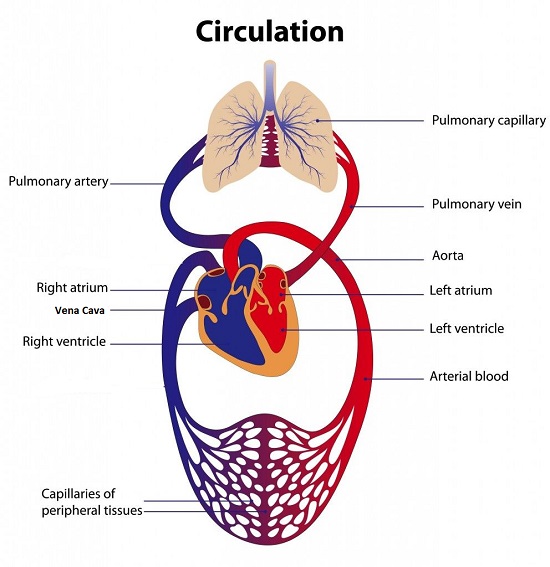
- The heart is a muscular organ located in the chest cavity. Its purpose is to pump blood to all parts of the body.
- It is divided into two main parts; the left side and the right side
- The heart is made up of 4 chambers; the upper two chambers are identified as
auricles while the bottom two chambers are identified as
ventricles.
- Four main blood vessels connect to the heart:
- Pulmonary artery
- Pulmonary vein
- Vena Cava
- Aorta

Cross-sectional picture of the heart
-
Deoxygenated blood from all parts of the body (except the lungs) enters the heart through the
vena cava, which is largest vein in the human body.
-
Oxygenated blood leaves the heart through the
aorta, which is the largest artery in the human body.
- The
right auricles receives blood from all parts of the body and directs it to the
right ventricle which pumps this blood to the lungs for
oxygenation. This blood is
carried to the lungs through the
pulmonary artery.
-
Oxygenated blood flows from the lungs to the
left auricle through the
pulmonary vein. It then flows to the
muscular left ventricle and is pumped to the rest of the body through the
aorta.